Retrofit注解详细探究
在Retrofit使用入门一文中,了解了Retrofit的基本使用。现在继续深挖Retrofit的核心:注解,Retrofit通过注解的方式将HTTP网络请求转换成Java接口。
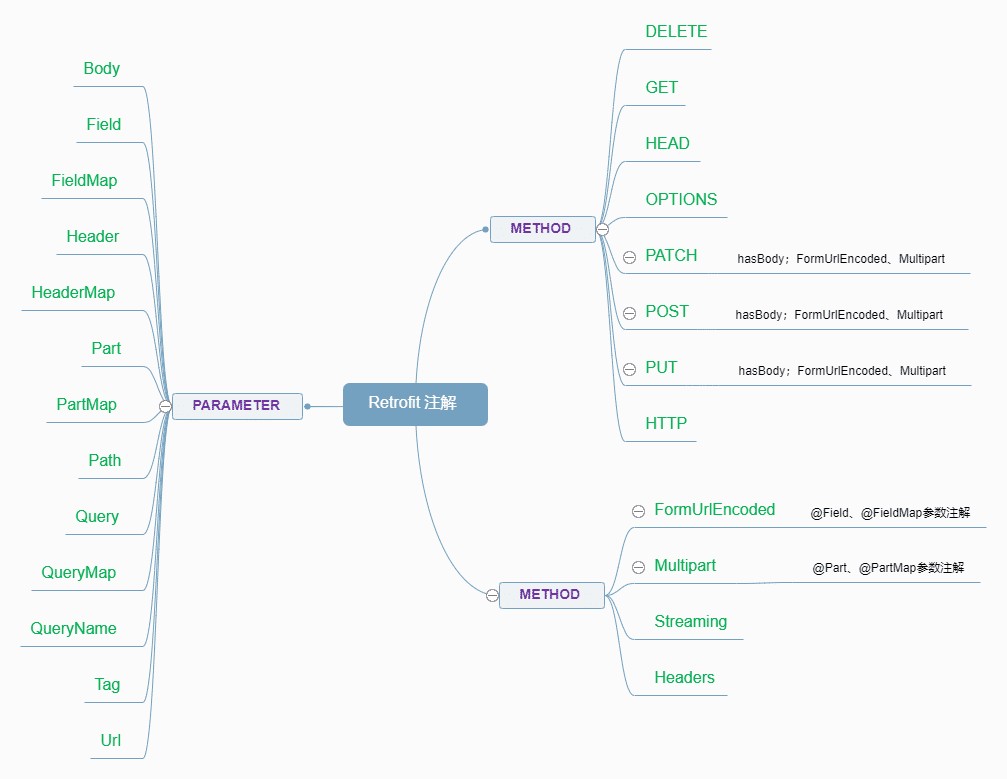
当前使用的Retrofit版本是2.9.0,这个版本共有25个注解。按照注解作用的地方可以分为两类:一类是方法注解(METHOD),作用在方法上。一类是参数注解(PARAMETER),用在方法的参数中。
1、方法注解
Retrofit用在方法上的注解共有12个:@DELETE、@GET、@HEAD、@OPTIONS、@PATCH、@POST、@PUT、@HTTP;@FormUrlEncoded、@Multipart、@Streaming、@Headers。
1.1、网络请求方法注解
在RESTful 统一接口一文,了解了HTPP网络请求的几种统一接口。Retrofit中的网络请求方法注解分别对应这几种HTTP请求方法。
1.1.1、@GET
@GET注解应用在方法上,表示该方法对应的HTTP网络请求是GET。
interface GetCall {
@GET("/info")
fun getCall(): Call<ResponseBody>
}返回类型Call<T>的泛型可以为原始响应类型ResponseBody或者空Void。
interface GetCall {
@GET("/info")
fun getCall(): Call<Void>
}T也可以是定义的Json实体类等其它类型,GsonConverter会将网络响应转换成为设置的返回结果类型T。
interface GetCall {
@GET("/info")
fun getCall(): Call<Bean>
}@GET注解不可与@FormUrlEncoded和@Multipart标记注解同时作用在方法上。因为GET不携带请求体,后面的@HEAD、@OPTIONS等注解也是一样的。
从源码可以发现,在RequestFactory类中的parseMethodAnnotation(Annotation annotation)方法解析注解,只允许PATCH、POST、PUT三个网络请求方法可以携带RequestBody请求体,至于@HTTP注解则看具体情况。
private void parseMethodAnnotation(Annotation annotation) {
if (annotation instanceof DELETE) {
parseHttpMethodAndPath("DELETE", ((DELETE) annotation).value(), false);
} else if (annotation instanceof GET) {
parseHttpMethodAndPath("GET", ((GET) annotation).value(), false);
} else if (annotation instanceof HEAD) {
parseHttpMethodAndPath("HEAD", ((HEAD) annotation).value(), false);
} else if (annotation instanceof PATCH) {
parseHttpMethodAndPath("PATCH", ((PATCH) annotation).value(), true);
} else if (annotation instanceof POST) {
parseHttpMethodAndPath("POST", ((POST) annotation).value(), true);
} else if (annotation instanceof PUT) {
parseHttpMethodAndPath("PUT", ((PUT) annotation).value(), true);
} else if (annotation instanceof OPTIONS) {
parseHttpMethodAndPath("OPTIONS", ((OPTIONS) annotation).value(), false);
} else if (annotation instanceof HTTP) {
HTTP http = (HTTP) annotation;
parseHttpMethodAndPath(http.method(), http.path(), http.hasBody());
}
...
}在build()构造Request请求的时候会结合前面解析出的请求方法和RequestBody进行判断,很多时候开发中遇到的异常是从这个方法中抛出的。
RequestFactory build() {
...
if (httpMethod == null) {
throw methodError(method, "HTTP method annotation is required (e.g., @GET, @POST, etc.).");
}
if (!hasBody) {
if (isMultipart) {
throw methodError(method,
"Multipart can only be specified on HTTP methods with request body (e.g., @POST).");}
if (isFormEncoded) {
throw methodError(method,
"FormUrlEncoded can only be specified on HTTP methods with request body (e.g., @POST).");}
}
...
if (relativeUrl == null && !gotUrl) {
throw methodError(method, "Missing either @%s URL or @Url parameter.", httpMethod);
}
if (!isFormEncoded && !isMultipart && !hasBody && gotBody) {
throw methodError(method, "Non-body HTTP method cannot contain @Body.");
}
if (isFormEncoded && !gotField) {
throw methodError(method, "Form-encoded method must contain at least one @Field.");
}
if (isMultipart && !gotPart) {
throw methodError(method, "Multipart method must contain at least one @Part.");
}
return new RequestFactory(this);
}扯远了,回来继续讲解注解。
1.1.2、@POST
@POST注解用来向服务端发送数据,可以携带RequestBody。
interface PostMessage {
@FormUrlEncoded
@POST("/report")
fun postMessage(@Query("name") name: String): Call<Boolean>
}1.1.3、@DELETE
@DELETE注解的方法不能携带RequestBody。返回值具体业务而定,可以是简单的Boolean(前提是转换器能自行转换),或者返回其它类型的数据通知删除结果。
interface DeleteService {
@DELETE("/storage/{fileName}")
fun deleteComments(@Path("fileName") fileName: String): Call<Boolean>
}涉及到的参数注解第2节会讲到。基本的HTTP请求方法,再结合Retrofit中其它参数注解完成丰富的API设计。
1.1.4、PUT
@PUT请求方法使用请求中的内容创建或者替换目标资源。
interface PutService {
@PUT("/table/info")
fun putInfo(): Call<Result>
}PUT与POST方法的区别在于,PUT方法是幂等的:调用一次与连续调用多次是等价的(即没有副作用)。而连续调用多次POST方法可能会有副作用,比如将一个订单重复提交多次。
1.1.5、PATCH
@PATCH用于对资源进行部分修改。
interface PatchService {
@FormUrlEncoded
@PATCH("/data/_table")
fun updateInfo(@FieldMap set: Map<String, String>): Call<String>
}1.1.6、HEAD
@HEAD注解用来请求资源的头部信息, 并且这些信息头与GET方法请求时返回的一致.。
interface HeadCall {
@HEAD("/")
fun getHead(): Call<Void>
}HEAD请求不会返回任何Body,因此Call<T>中的泛型必须为Void空。Kotlin中的Unit空类型暂时并不被Retrofit库支持。
interface HeadCall {
@HEAD("/")
fun getHead(): Call<Unit>
}从Retrofit源码中的注释,可以看到Retrofit开发团队也在计划准备支持一下Kotlin的空类型Unit。
// TODO support Unit for Kotlin?
if (requestFactory.httpMethod.equals("HEAD") && !Void.class.equals(responseType)) {
throw methodError(method, "HEAD method must use Void as response type.");
}使用HEAD请求方法的一个场景是在下载一个大文件前先获取header头部少量信息,知道文件大小再决定是否要下载, 以此可以节约带宽资源。这个做法有点像解析Bitmap,先用inSampleSize获取图片的大小,再压缩采样加载Bitmap。
{
cache-control=[no-store, no-cache, must-revalidate],
connection=[keep-alive],
content-encoding=[gzip],
content-type=[text/html; charset=utf-8],
date=[Tue, 30 Mar 2021 12:32:59 GMT],
expires=[Thu, 19 Nov 1981 08:52:00 GMT],
pragma=[no-cache], server=[nginx],
set-cookie=[bbs_sid=ll7d8fb8okit2c6ctqnfif85pb; expires=Thu,
08-Jul-2021 12:32:59 GMT; Max-Age=8640000; HttpOnly,
cookie_test=tMWidLYc5m6_2BXD53ZuiXdvh5C7s5_2BLL9_2BthuaOhZE8_2B5afYo;
expires=Wed, 31-Mar-2021 12:32:59 GMT; Max-Age=86400],
vary=[Accept-Encoding],
x-powered-by=[PHP/7.3.9]
}1.1.7、OPTIONS
@OPTIONS注解的方法用于获取目的服务端所支持的通信选项。不能包含RequestBody,且返回类型为Void/Unit空。
interface OPTIONS_Options {
@OPTIONS("/")
fun getOptions(): Call<Void>
}举个例子:
val retrofit = retrofit.newBuilder()
.baseUrl("http://example.org/")
.build()
val options: OPTIONS_Options = retrofit.create(OPTIONS_Options::class.java)
val call = options.getOptions()
call.enqueue(object : Callback<Void> {
override fun onResponse(call: Call<Void>, response: Response<Void>) {
Log.d(TAG,"options onResponse ${response.headers().toMultimap().toString()}")
}
override fun onFailure(call: Call<Void>, t: Throwable) {
}
})响应报文包含一个 allow 首部字段,该字段的值表明了服务器支持的所有 HTTP 方法:[OPTIONS, GET, HEAD, POST]。测试链接:http://example.org/。
{
allow=[OPTIONS, GET, HEAD, POST],
cache-control=[max-age=604800],
content-length=[0],
content-type=[text/html; charset=UTF-8],
date=[Wed, 31 Mar 2021 03:29:39 GMT],
expires=[Wed, 07 Apr 2021 03:29:39 GMT],
server=[EOS (vny/0452)]
}
1.1.8、HTTP
@HTTP注解用来替换@GET、@POST、@DELETE、@PUT、@HEAD等注解,用来自定义用户请求,使用@HTTP注解可以拓展网络请求功能。
interface HttpService {
@HTTP(method = "GET",path = "/search",hasBody = false)
fun commonHttpMethod(@Query("keywords") keyword: String): Call<MusicBean>
}@HTTP注解需要设置method、path、hasBody。必须要设置请求方法method,默认无RequestBody。在Retrofit内部构造请求Request的时候会用到开发者自定义HTTP中设置的这三个属性。
private void parseMethodAnnotation(Annotation annotation) {
...
else if (annotation instanceof HTTP) {
HTTP http = (HTTP) annotation;
parseHttpMethodAndPath(http.method(), http.path(), http.hasBody());
}
...
}1.2、其它方法注解
以上8个是基本的HTTP网络请求方法注解,另外还有4个方法注解,用来标记RequestBody类型、Response响应类型以及添加请求头Headers。
1.2.1、@FormUrlEncoded
@FormUrlEncoded注解只能用在有RequestBody的网络请求方法上,比如使用@POST、@PUT、@PATCH注解的请求方法。
RequestFactory build() {
...
if (!hasBody) {
...
if (isFormEncoded) {
throw methodError(
method,
"FormUrlEncoded can only be specified on HTTP methods with "
+ "request body (e.g., @POST).");
}
}
...
return new RequestFactory(this);
}@FormUrlEncoded注解的方法必须至少包含一个@Field注解参数,关于@Field注解详见2.2节。
RequestFactory build() {
...
if (!isFormEncoded && !isMultipart && !hasBody && gotBody) {
throw methodError(method, "Non-body HTTP method cannot contain @Body.");
}
if (isFormEncoded && !gotField) {
throw methodError(method, "Form-encoded method must contain at least one @Field.");
}
if (isMultipart && !gotPart) {
throw methodError(method, "Multipart method must contain at least one @Part.");
}
return new RequestFactory(this);
}举个例子,提交评论的接口设计如下:
interface PostService {
@FormUrlEncoded
@POST("/user/comment")
fun postComments(@Field("comments") comments: String): Call<String>
}1.2.2、Multipart
和@FormUrlEncoded一样,@Multipart注解只能用在有请求体的网络请求方法参数中。否则会抛出异常:Multipart can only be specified on HTTP methods with request body。
RequestFactory build() {
...
if (!hasBody) {
if (isMultipart) {
throw methodError(
method,
"Multipart can only be specified on HTTP methods with request body (e.g., @POST).");
}
...
}
...
return new RequestFactory(this);
} 同样的,@Multipart注解的方法也必须至少包含一个@Part注解的参数。否则抛出异常:Multipart method must contain at least one @Part。关于@Part注解详见2.6节。
if (isMultipart && !gotPart) {
throw methodError(method, "Multipart method must contain at least one @Part.");
} 举个例子:上传文件的接口设计:
interface PostFileService {
@Multipart
@POST("/")
fun uploadFile(@Part filePart: MultipartBody.Part): Call<String>
}文件上传部分逻辑代码实例:
//从待上传文件创建RequestBody
val requestBody = File(imagePath).asRequestBody("image/png".toMediaType())
val head: Headers = Headers.Builder().add("content-lenght", "128kb").build()
//构造携带文件请求体的MultipartBody.Part
val part: MultipartBody.Part = MultipartBody.Part.create(head, requestBody)
//通过接口上传文件
val call = uploadService.uploadFile(part)1.2.3、Streaming
@Streaming注解的网络请求,响应数据以OKHttp中原始ResponseBody的形式返回。对于没有@Streaming注解的方法,则先将响应数据全部获取到内存中处理(比如使用转换器将原始响应转换成合适的类型)。@Streaming注解适合大文件下载场景。
interface BigFileDownloadService {
@Streaming
@GET("/{path}")
fun downloadBigFile(@Path("path") file: String): Call<ResponseBody>
}使用@Steaming注解实现大文件下载示例,文件为Qt安装包,约3.2Gb:
/**
* https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/qt/official_releases/qt/5.12/5.12.0/qt-opensource-mac-x64-5.12.0.dmg
* https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/
* qt/official_releases/qt/5.12/5.12.0/qt-opensource-mac-x64-5.12.0.dmg
*/
val retrofit = Retrofit.Builder()
.addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create())
.baseUrl("https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/")
.build()
val downloadService: BigFileDownloadService =
retrofit.create(BigFileDownloadService::class.java)
val filePath = "qt/official_releases/qt/5.12/5.12.0/qt-opensource-mac-x64-5.12.0.dmg"
val call = downloadService.downloadBigFile(filePath)
call.enqueue(object : Callback<ResponseBody> {
override fun onResponse(call: Call<ResponseBody>, response: Response<ResponseBody>) {
//从Response流中处理大文件下载
}
override fun onFailure(call: Call<ResponseBody>, t: Throwable) {
}
})1.2.4、Headers
通常还会在请求头中添加一些特殊的消息,Retrofit提供两种添加Headers信息的方式。第一种就是通过给方法添加@Headers注解,向Headers中添加静态无法修改的消息报头。另一种方法通过方法注解动态增加请求头信息,详见2.4节和2.5节。
interface GetCall {
@Headers("Cache-Control: max-age=640000", "cache-control: no-cache")
@GET("/popular")
fun getPopular(): Call<Bean>
}2、参数注解
作用在参数上的注解有:@Body、@Field、@FieldMap、@Header、@HeaderMap、@Part、@PartMap、@Path、@Query、@QueryMap、@QueryName、@Tag、@Url。
在接口中定义的请求方法如果是有参方法,参数必须用上面的参数注解。否则RequestFactory解析interface中方法的参数时,调用parseParameter(...)方法会校验报错:No Retrofit annotation found。
2.1、@Body
@Body注解用于非表单请求体。有一些注意坑点,开发者在使用过程中可能会踩到。
interface GetCall {
@POST("/search")
fun postCall(@Body key: String): Call<Void>
}只能作用在有RequestBody的网络请求方法上,不能用于GET、HEAD等没有请求体的网络请求方法中。否则会抛出Non-body HTTP method cannot contain @Body.异常。
RequestFactory build() {
...
if (!isFormEncoded && !isMultipart && !hasBody && gotBody) {
throw methodError(method, "Non-body HTTP method cannot contain @Body.");
}
...
return new RequestFactory(this);
}@Body注解不能作用在已经被@FormUrlEncoded和@Multipart注解过的方法的参数中。否则会抛出@Body parameters cannot be used with form or multi-part encoding.异常。
private ParameterHandler<?> parseParameterAnnotation(...) {
...
if (isFormEncoded || isMultipart) {
throw parameterError(
method, p, "@Body parameters cannot be used with form or multi-part encoding.");
}
...
}2.2、@Field
@Field注解用于向表单提交字段。
interface Post_interface {
@FormUrlEncoded
@POST("/name")
fun getInfo(@Field("name") name: String): Call<String>
}只能用在@FormUrlEncoded注解的方法的参数中。否则会抛出异常:@Field parameters can only be used with form encoding。
@Nullable
private ParameterHandler<?> parseParameterAnnotation(
int p, Type type, Annotation[] annotations, Annotation annotation) {
...
else if (annotation instanceof Field) {
validateResolvableType(p, type);
if (!isFormEncoded) {
throw parameterError(method, p, "@Field parameters can only be used with form encoding.");
}
...
return new ParameterHandler.Tag<>(tagType);
}
return null; // Not a Retrofit annotation.
}2.3、@FieldMap
@FieldMap同上面的@Field注解一样,用于@FormUrlEncoded注解的表单请求提交字段。
interface PostMap {
@FormUrlEncoded
@POST("/info")
fun getInfo(@FieldMap info: Map<String, String>): Call<String>
}@FieldMap注解的参数必须是Map类型,否则会抛出异常:@FieldMap parameter type must be Map.
private ParameterHandler<?> parseParameterAnnotation(
int p, Type type, Annotation[] annotations, Annotation annotation) {
...
else if (annotation instanceof FieldMap) {
validateResolvableType(p, type);
if (!isFormEncoded) {
throw parameterError(
method, p, "@FieldMap parameters can only be used with form encoding.");
}
Class<?> rawParameterType = Utils.getRawType(type);
if (!Map.class.isAssignableFrom(rawParameterType)) {
throw parameterError(method, p, "@FieldMap parameter type must be Map.");
}
...
}2.4、@Header
@Header参数注解用于给请求添加一个请求头。传入的参数值如果为null,则忽略。可以为List集合,每一个非空项都被添加到请求头中。
interface GetInfoService {
@GET("/info")
fun getInfo(@Header("Accept-Language") language: String): Call<String>
} 请求头中的相同name的value不会互相覆盖,是可以重复的。这一点“得益”于OkHttp中Headers头部信息的存储方式实现,详见OKHttp之Headers请求头。
2.5、@HeaderMap
@HeaderMap和@Header注解一样用来添加请求头,能够批量添加信息头。
interface GetInfoService {
@GET("/info")
fun getInfo(@HeaderMap map: Map<String, String>): Call<String>
}@HeaderMap注解的参数必须是Map,且键类型必须是String。这些在源码中都会校验,如果不符合就会抛出异常:
private ParameterHandler<?> parseParameterAnnotation(...) {
...
else if (annotation instanceof HeaderMap) {
...
Class<?> rawParameterType = Utils.getRawType(type);
if (!Map.class.isAssignableFrom(rawParameterType)) {
throw parameterError(method, p, "@HeaderMap parameter type must be Map.");
}
...
if (String.class != keyType) {
throw parameterError(method, p, "@HeaderMap keys must be of type String: " + keyType);
}
...
}2.6、@Part
@Part参数注解表示multi-part多块请求的一部分。参数类型可以是:MultipartBody.Part、RequestBody或者其它类型。
①如果类型为MultipartBody.Part,则内容将直接使用。
②如果类型为RequestBody,则该值将直接与其内容类型一起使用。
③其类型不是以上两种而是其它对象类型,将通过使用Converter转换为适当的表示形式。
interface PostPartService {
@Multipart
@POST("/upload")
fun getInfo(@Part("file") request: RequestBody): Call<String>
}@Part注解只能和@Multipart注解一起使用,否则会抛出异常:@Part parameters can only be used with multipart encoding。还记得:在1.2.2节提到Multipart注解只能在有RequestBody的HTTP方法上使用,比如使用POST、PUT、PATCH注解的请求方法。
@Part注解的参数类型如果是MultipartBody.Part,则不能给注解传入参数值。但@Part注解的参数类型如果不是MultipartBody.Part,而是RequestBody或者其它类型,则必须给@Part注解传入name值。否则又会抛出异常:@Part annotation must supply a name or use MultipartBody.Part parameter type。
private ParameterHandler<?> parseParameterAnnotation(...) {
...
else if (annotation instanceof Part) {
validateResolvableType(p, type);
if (!isMultipart) {
throw parameterError(
method, p, "@Part parameters can only be used with multipart encoding.");
}
Part part = (Part) annotation;
...
if (!MultipartBody.Part.class.isAssignableFrom(Utils.getRawType(iterableType))) {
throw parameterError(
method,
p,
"@Part annotation must supply a name or use MultipartBody.Part parameter type.");
}
...
}
2.7、@PartMap
@PartMap注解和上一节中的@Part注解作用相似,支持多块上传。所以适合文件分块、多文件上传的业务场景。
interface PostMultiFile {
@Multipart
@POST("/upload")
fun uploadFile(@PartMap key: Map<String, String>): Call<Void>
}@PartMap注解的参数类型必须是Map,否则会抛出异常:@PartMap parameter type must be Map。在源码RequestFactory类中的parseParameterAnnotation()方法中解析校验各个参数注解。
...
if (!Map.class.isAssignableFrom(rawParameterType)) {
throw parameterError(method, p, "@PartMap parameter type must be Map.");
}
...@PartMap注解的Map映射参数中的键类型必须是String类型,否则会抛出异常:@PartMap keys must be of type String。
if (String.class != keyType) {
throw parameterError(method, p, "@PartMap keys must be of type String: " + keyType);
}2.8、@Path
@Path参数注解用于URL地址的缺省值。
interface PostMultiFile {
@POST("/upload/{path}")
fun uploadFile(@Path("path") path: String): Call<Void>
}缺省{path}的命名必须符合正则:[a-zA-Z][a-zA-Z0-9_-]*。否则在validatePathName(int p, String name)方法中校验path不通过会抛出异常:@Path parameter name must match \{([a-zA-Z][a-zA-Z0-9_-]*)\}。
// Upper and lower characters, digits, underscores, and hyphens, starting with a character.
private static final String PARAM = "[a-zA-Z][a-zA-Z0-9_-]*";
private static final Pattern PARAM_NAME_REGEX = Pattern.compile(PARAM);
...
private void validatePathName(int p, String name) {
if (!PARAM_NAME_REGEX.matcher(name).matches()) {
throw parameterError(
method,
p,
"@Path parameter name must match %s. Found: %s",
PARAM_URL_REGEX.pattern(),
name);
}
// Verify URL replacement name is actually present in the URL path.
if (!relativeUrlParamNames.contains(name)) {
throw parameterError(method, p, "URL \"%s\" does not contain \"{%s}\".", relativeUrl, name);
}
}@Path注解必须要传入和URL中{path}一样的名称,否则会找不到替换的缺省路径会报异常。比如反例:
interface PostMultiFile {
@POST("/upload/{path1}")
fun uploadFile(@Path("path2") path: String): Call<Void>
}上面这样的API设计就不符合规范,报错: URL "/upload/{path1}" does not contain "{path2}"。
2.9、@Query
@Query注解的参数会作为查询参数附加到URL。@Query用法简单,问题不大。但是因为参数值直接附加到URL上,所以安全性较低,敏感数据最好用POST方式并且加密。
interface QueryService {
@POST("/info")
fun queryName(@Query("name") name: String): Call<Void>
}上面这个例子访问的服务端路径是/info?name=name。@Query一般用来进行简单的查询,必须要指定注解的value值。
2.10、@QueryMap
@QueryMap参数注解和上面的@Query一样,都是用于查询。借助Map映射可以携带更多的信息。
interface QueryService {
@GET("/info")
fun queryName(@QueryMap map: Map<String, String>): Call<Void>
}@QueryMap注解的参数类型必须是Map映射,同时映射的键必须是String类型。否则会抛出异常:@QueryMap parameter type must be Map. 或 @QueryMap keys must be of type String: class。
2.11、@QueryName
@QueryName注解的参数会附加到不需要值的查询URL上。参数名称默认开启URL编码。
interface QueryService {
@GET("/info")
fun queryName(@QueryName(encoded = true) map: String): Call<Void>
}
2.12、@Tag
@Tag注解使用类型作为键,将参数实例添加为请求标记,不允许重复的Tag标签类型。
interface QueryService {
@GET("/info")
fun queryName(@Tag type: String): Call<Void>
}标记的参数值如果为null,将从请求中省略。 传递参数化类型(例如List<String>)将使用原始类型(即List.class)作为键。
2.13、@Url
@Url注解的参数将作为请求路径URL,请求方法注解无需再设置URL。
interface QueryService {
@GET
fun queryUrl(@Url url: String): Call<Void>
}25种注解要熟练掌握,各注解之间的依赖和互斥也要非常清楚。