uptime 查看系统运行时间
记录一个命令:uptime。直接输入该命令,会得到系统当前时间、系统运行了多长时间、登录用户数量以及过去 1、5 和 15 分钟的系统负载平均值。
uptime
12:56:15 up 11 days, 10 min, 0 users, load average: 50.39, 50.68, 50.90
这个命令不光可以了解系统启动时间,还可以了解当前系统的负载状况。
如果不熟悉一个命令的用法,通常用--help选项快速了解一个命令的用法。
uptime --help
usage: uptime [-ps]
Tell the current time, how long the system has been running, the number
of users, and the system load averages for the past 1, 5 and 15 minutes.
-p Pretty (human readable) uptime
-s Since when has the system been up?
加上-p选项,阅读友好的形式显示系统启动时间,按:周,日,时,分。
uptime -p
up 1 week, 4 days, 0 hours, 10 minutes
结合-s选项,显示系统是从什么时候开始启动的。
uptime -s
2021-06-17 12:46:07
设置里也使用到了系统启动时间,在关于手机 > 状态信息 > 开机时间中查看:
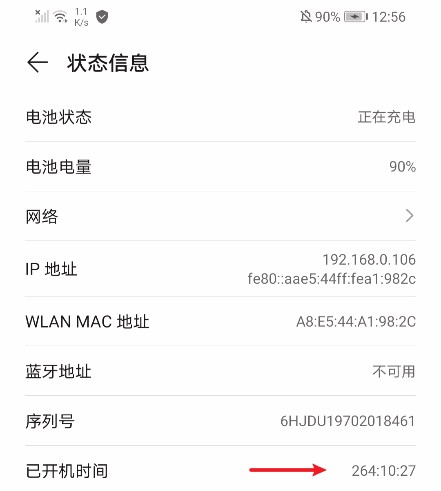
查看源码,这里是通过SystemClock获取系统启动时间,由native层uptimeMillis()方法实现。先去JNI层,在/frameworks/base/core/jni/目录下,从android_os_SystemClock.cpp找到注册的native方法
static const JNINativeMethod gMethods[] = {
// All of these are @CriticalNative, so we can defer directly to SystemClock.h for
// some of these
{ "uptimeMillis", "()J", (void*) uptimeMillis },
...
}; 去/system/core/libutils/目录下找到SystemClock.cpp,其中实现了uptimeMillis()方法
/*
* native public static long uptimeMillis();
*/
int64_t uptimeMillis()
{
int64_t when = systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC);
return (int64_t) nanoseconds_to_milliseconds(when);
} 调用/system/core/libutils/库中Timers.cpp的systemTime()方法
nsecs_t systemTime(int clock)
{
static const clockid_t clocks[] = {
CLOCK_REALTIME,
CLOCK_MONOTONIC,
CLOCK_PROCESS_CPUTIME_ID,
CLOCK_THREAD_CPUTIME_ID,
CLOCK_BOOTTIME
};
struct timespec t;
t.tv_sec = t.tv_nsec = 0;
clock_gettime(clocks[clock], &t);
return nsecs_t(t.tv_sec)*1000000000LL + t.tv_nsec;
} 众所周知Android基于Linux内核,再往下就是调用time.h中定义的Linux库函数clock_gettime(),该函数是基于Linux C语言的时间函数,可以用于计算精度和纳秒。
到这里就结束,别往下刨了。熟悉源码结构,看源码就像顺藤摸瓜,源码结构详见熟悉Android源码目录结构一文。