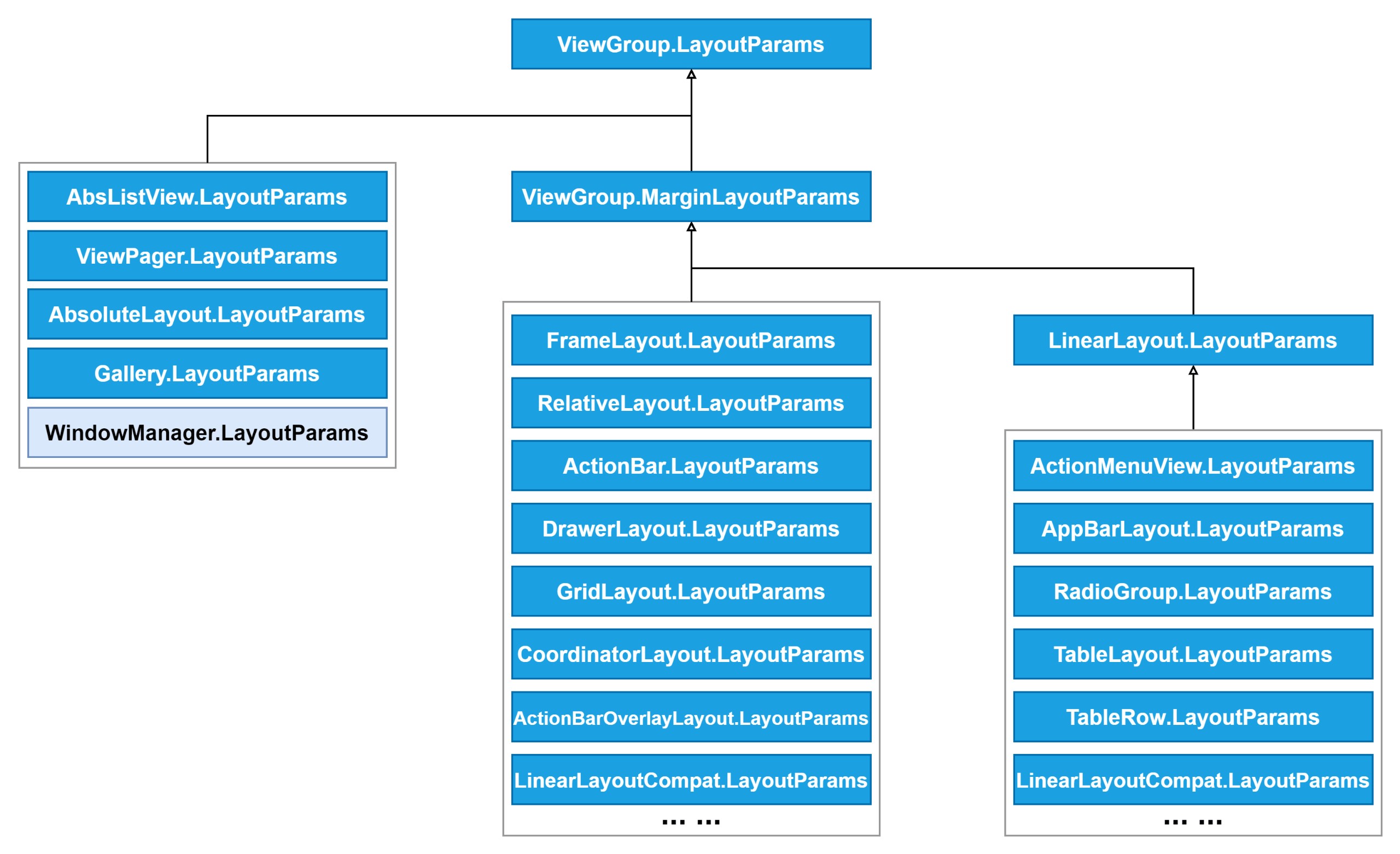
View布局参数LayoutParams
为了计算布局实现动效和LayoutParams密切接触有一段时间,LayoutParams彻底玩明白了。
1、LayoutParams
LayoutParams直译为布局参数,是定义在ViewGroup中的静态内部类。
1.1、LayoutParams用途
LayoutParams类的注释清楚的写明此类的用途:LayoutParams是子View用来告诉它们的父布局如何放置自己。
/**
* LayoutParams are used by views to tell their parents how they want to be
* laid out. See
* {@link android.R.styleable#ViewGroup_Layout ViewGroup Layout Attributes}
* for a list of all child view attributes that this class supports.
*/1.2、继承关系
定义在ViewGroup中的LayoutParams类是各种子LayoutParams的基类,只定义View的两个基本属性:宽度和高度。
/**
* There are subclasses of LayoutParams for different subclasses of
* ViewGroup. For example, AbsoluteLayout has its own subclass of
* LayoutParams which adds an X and Y value.</p>
*
* <div class="special reference">
* <h3>Developer Guides</h3>
* <p>For more information about creating user interface layouts, read the
* <a href="{@docRoot}guide/topics/ui/declaring-layout.html">XML Layouts</a> developer
* guide.</p></div>
*
* @attr ref android.R.styleable#ViewGroup_Layout_layout_height
* @attr ref android.R.styleable#ViewGroup_Layout_layout_width
*/继承抽象类ViewGroup的容器实现类非常多,比如常见的LinearLayout、RelativeLayout、FrameLayout等等。
有些容器在继承ViewGroup的同时,还会继承ViewGroup.LayoutParams实现自己的LayoutParams。或者直接使用父类的LayoutParams。
2、LayoutParams类详解
通过前面简单的了解,定义在ViewGroup中的LayoutParams基类只有宽高两个基本信息。
2.1、宽 & 高
ViewGroup中的LayoutParams基类只定义了View的两个基本属性:width和height,控件的宽和高。
/** * Information about how wide the view wants to be. Can be one of the * constants FILL_PARENT (replaced by MATCH_PARENT * in API Level 8) or WRAP_CONTENT, or an exact size. */ public int width; /** * Information about how tall the view wants to be. Can be one of the * constants FILL_PARENT (replaced by MATCH_PARENT * in API Level 8) or WRAP_CONTENT, or an exact size. */ public int height; /** * 用于动画布局。 */ public LayoutAnimationController.AnimationParameters layoutAnimationParameters;
关于ViewGroup.LayoutParams中对于View宽高的说明如下,值只能是以下三种情况之一:①MATCH_PARENT、②WRAP_CONTENT、③具体的值。
/** * <p> * The base LayoutParams class just describes how big the view wants to be * for both width and height. For each dimension, it can specify one of: * <ul> * <li>FILL_PARENT (renamed MATCH_PARENT in API Level 8 and higher), which * means that the view wants to be as big as its parent (minus padding) * <li> WRAP_CONTENT, which means that the view wants to be just big enough * to enclose its content (plus padding) * <li> an exact number * </ul> */
有没有很熟悉?这也是XML布局中最常用的两个属性,以layout_前缀加上布局参数的属性。看到以layout_前缀开头的属性,就应该知道这个属性来自LayoutParams。
<TextView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="18dp" /> <TextView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
2.2、MATCH_PARENT和WRAP_CONTENT
ViewGroup.LayoutParams中定义了两个描述MATCH_PARENT和WRAP_CONTENT的常量。对于已废弃的FILL_PARENT直接忽略,用MATCH_PARENT替代。
/**
* Special value for the height or width requested by a View.
* FILL_PARENT means that the view wants to be as big as its parent,
* minus the parent's padding, if any. This value is deprecated
* starting in API Level 8 and replaced by {@link #MATCH_PARENT}.
*/
@SuppressWarnings({"UnusedDeclaration"})
@Deprecated
public static final int FILL_PARENT = -1;
/**
* Special value for the height or width requested by a View.
* MATCH_PARENT means that the view wants to be as big as its parent,
* minus the parent's padding, if any. Introduced in API Level 8.
*/
public static final int MATCH_PARENT = -1;
/**
* Special value for the height or width requested by a View.
* WRAP_CONTENT means that the view wants to be just large enough to fit
* its own internal content, taking its own padding into account.
*/
public static final int WRAP_CONTENT = -2;2.3、LayoutParams的三个构造方法
ViewGroup.LayoutParams有三个公有构造方法,用来构造ViewGroup.LayoutParams实例。LayoutParams子类也要实现这三个父类构造方法。
/**
* Creates a new set of layout parameters. The values are extracted from
* the supplied attributes set and context. The XML attributes mapped
* to this set of layout parameters are:
*
* <ul>
* <li><code>layout_width</code>: the width, either an exact value,
* {@link #WRAP_CONTENT}, or {@link #FILL_PARENT} (replaced by
* {@link #MATCH_PARENT} in API Level 8)</li>
* <li><code>layout_height</code>: the height, either an exact value,
* {@link #WRAP_CONTENT}, or {@link #FILL_PARENT} (replaced by
* {@link #MATCH_PARENT} in API Level 8)</li>
* </ul>
*
* @param c the application environment
* @param attrs the set of attributes from which to extract the layout
* parameters' values
*/
public LayoutParams(Context c, AttributeSet attrs) {
TypedArray a = c.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.ViewGroup_Layout);
setBaseAttributes(a,
R.styleable.ViewGroup_Layout_layout_width,
R.styleable.ViewGroup_Layout_layout_height);
a.recycle();
}用已知的宽、高构造ViewGroup.LayoutParams对象。LayoutParams子类中也有类似的构造方法。
/**
* Creates a new set of layout parameters with the specified width
* and height.
*
* @param width the width, either {@link #WRAP_CONTENT},
* {@link #FILL_PARENT} (replaced by {@link #MATCH_PARENT} in
* API Level 8), or a fixed size in pixels
* @param height the height, either {@link #WRAP_CONTENT},
* {@link #FILL_PARENT} (replaced by {@link #MATCH_PARENT} in
* API Level 8), or a fixed size in pixels
*/
public LayoutParams(int width, int height) {
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}用已有的LayoutParams作为参数构造新的LayoutParams对象,俗称复制构造函数。
/**
* Copy constructor. Clones the width and height values of the source.
*
* @param source The layout params to copy from.
*/
public LayoutParams(LayoutParams source) {
this.width = source.width;
this.height = source.height;
}还有一个无参构造方法,框架内部使用,应用开发者无法使用,了解一下即可。
/**
* Used internally by MarginLayoutParams.
* @hide
*/
@UnsupportedAppUsage
LayoutParams() {
}3、派生LayoutParams
不能直接使用ViewGroup.LayoutParams类,往往使用其子类。在第1.2节中就已经提到过,在众多继承ViewGroup的容器类中,也有不少派生LayoutParams类。
3.1、MarginLayoutParams
绝大部分派生LayoutParams并不是直接继承自ViewGroup.LayoutParams,而是继承自ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams。给原本只有width和height的布局参数,增加了四个额外的参数:left、top、right、bottom,表示View上下左右四个方向的空白边距。
public static class MarginLayoutParams extends ViewGroup.LayoutParams {
public int leftMargin;
public int topMargin;
public int rightMargin;
public int bottomMargin;
private int startMargin = DEFAULT_MARGIN_RELATIVE;
private int endMargin = DEFAULT_MARGIN_RELATIVE;
... ...
}这也是除了2.1节中提到的两个属性之外,在XML布局中常用到的几个layout_属性:
<TextView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_margin="30dp" android:layout_marginHorizontal="20dp" android:layout_marginVertical="20dp" android:layout_marginLeft="10dp" android:layout_marginTop="10dp" android:layout_marginRight="10dp" android:layout_marginBottom="10dp" android:layout_marginStart="10dp" android:layout_marginEnd="10dp" />
后来为了更好的支持RTL,带有强烈固定方向含义的left和right被start和end取代。建议不要用含有left和start的属性,而应该用含有start和end的属性,可以更好的支持RTL。
最后,来看一下ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams的构造函数,从这里面可以更加清晰了解到前面布局中设置的几个margin属性设置流程:
①如果设置了layout_margin,那么用这个作为四个方向的统一边距值,即便设置了其它四个属性也不会生效。
②如果设置了垂直layout_marginVertical,那么layout_marginTop和layout_marginBottom属性将不起作用。
③同样的,如果设置了水平layout_marginHorizontal,那么layout_marginLeft和layout_marginRight属性将不起作用。
④layout_marginStart和layout_marginEnd不受除layout_margin之外的属性影响。
public MarginLayoutParams(Context c, AttributeSet attrs) {
super();
TypedArray a = c.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.ViewGroup_MarginLayout);
setBaseAttributes(a,
R.styleable.ViewGroup_MarginLayout_layout_width,
R.styleable.ViewGroup_MarginLayout_layout_height);
int margin = a.getDimensionPixelSize(
com.android.internal.R.styleable.ViewGroup_MarginLayout_layout_margin, -1);
//如果设置了layout_margin,那么用这个作为四个方向的统一边距值,即便设置了其它四个属性也不会生效。
if (margin >= 0) {
leftMargin = margin;
topMargin = margin;
rightMargin= margin;
bottomMargin = margin;
} else {
int horizontalMargin = a.getDimensionPixelSize(
R.styleable.ViewGroup_MarginLayout_layout_marginHorizontal, -1);
int verticalMargin = a.getDimensionPixelSize(
R.styleable.ViewGroup_MarginLayout_layout_marginVertical, -1);
if (horizontalMargin >= 0) {
leftMargin = horizontalMargin;
rightMargin = horizontalMargin;
} else {
leftMargin = a.getDimensionPixelSize(
R.styleable.ViewGroup_MarginLayout_layout_marginLeft,
UNDEFINED_MARGIN);
if (leftMargin == UNDEFINED_MARGIN) {
mMarginFlags |= LEFT_MARGIN_UNDEFINED_MASK;
leftMargin = DEFAULT_MARGIN_RESOLVED;
}
rightMargin = a.getDimensionPixelSize(
R.styleable.ViewGroup_MarginLayout_layout_marginRight,
UNDEFINED_MARGIN);
if (rightMargin == UNDEFINED_MARGIN) {
mMarginFlags |= RIGHT_MARGIN_UNDEFINED_MASK;
rightMargin = DEFAULT_MARGIN_RESOLVED;
}
}
startMargin = a.getDimensionPixelSize(
R.styleable.ViewGroup_MarginLayout_layout_marginStart,
DEFAULT_MARGIN_RELATIVE);
endMargin = a.getDimensionPixelSize(
R.styleable.ViewGroup_MarginLayout_layout_marginEnd,
DEFAULT_MARGIN_RELATIVE);
if (verticalMargin >= 0) {
topMargin = verticalMargin;
bottomMargin = verticalMargin;
} else {
topMargin = a.getDimensionPixelSize(
R.styleable.ViewGroup_MarginLayout_layout_marginTop,
DEFAULT_MARGIN_RESOLVED);
bottomMargin = a.getDimensionPixelSize(
R.styleable.ViewGroup_MarginLayout_layout_marginBottom,
DEFAULT_MARGIN_RESOLVED);
}
if (isMarginRelative()) {
mMarginFlags |= NEED_RESOLUTION_MASK;
}
}
...
}3.2、自定义LayoutParams
开发者可以继承ViewGroup.LayoutParams抽象类或者ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams类,实现自己的LayoutParams布局参数。
public class QuibblerView extends ViewGroup {
...
public static class LayoutParams extends ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams {
int front;
int behind;
public LayoutParams(Context c, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(c, attrs);
TypedArray a = c.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.QuibblerView_Layout);
front = a.getLayoutDimension(R.styleable.QuibblerView_Layout_layout_front, "layout_front");
behind = a.getLayoutDimension(R.styleable.QuibblerView_Layout_layout_behind, "layout_behind");
a.recycle();
}
public LayoutParams(int width, int height) {
super(width, height);
}
public LayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams source) {
super(source);
}
}
}再或者省点事,继承现有容器的LayoutParams,只需新增属性方法实现功能。比如直接继承LinearLayout中的LinearLayout.LayoutParams,在很多继承自LinearLayout的容器中也常常看到这样的做法:直接使用父容器的LayoutParams,或者继承父容器的LayoutParams。
public static class LayoutParams extends LinearLayout.LayoutParams {
public LayoutParams(Context c, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(c, attrs);
}
public LayoutParams(int width, int height) {
super(width, height);
}
public LayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams source) {
super(source);
}
}为了让自定义布局参数更方便些,再自定义一些xml属性。关于自定义</declare-styleable>属性详见《自定义View属性》一文。
<declare-styleable name="QuibblerView_Layout"> <attr name="layout_front" format="dimension" /> <attr name="layout_behind" format="dimension" /> </declare-styleable>
在LayoutParams构造方法中解析设置的xml属性:
public static class LayoutParams extends ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams {
int front;
int behind;
public LayoutParams(Context c, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(c, attrs);
TypedArray a = c.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.QuibblerView_Layout);
front = a.getLayoutDimension(R.styleable.QuibblerView_Layout_layout_front, "layout_front");
behind = a.getLayoutDimension(R.styleable.QuibblerView_Layout_layout_behind, "layout_behind");
a.recycle();
}
...
}4、使用LayoutParams
开发者无需自己构造LayoutParams设置给View,给View设置LayoutParams是该View所在父容器的责任,在随后文章中会详细讲到。
4.1、获取View的布局参数
通常是直接通过View的getLayoutParams()方法获取View中已有的布局参数:
ViewGroup.LayoutParams layoutParams = view.getLayoutParams();
每个View中都定义了一个ViewGroup.LayoutParams类型的属性成员mLayoutParams;
public ViewGroup.LayoutParams getLayoutParams() {
return mLayoutParams;
}4.2、修改布局参数
然后重新设置一些布局参数,如宽高、margin等。对于ViewGroup.LayoutParams布局参数也只有宽高属性可以设置。
layoutParams.height = height ; layoutParams.width = width ;
如需设置额外的属性,需要将从View拿到的ViewGroup.LayoutParams类型转换成View所在父布局中LayoutParams的类型或其超类。比如,在LinearLayout容器中的View,其布局参数类型为LinearLayout.LayoutParams。可以进行如下操作:
LinearLayout.LayoutParams layoutParams = (LinearLayout.LayoutParams) view.getLayoutParams(); layoutParams.setMargins(left, top, right, bottom); layoutParams.bottomMargin = 20; layoutParams.gravity = Gravity.END;
4.3、设置View的布局参数
最后,将设置过的LayoutParams再重新设置给View。有些开发者会遇到不设置不生效的情况,或者不二次设置也能生效。
view.setLayoutParams(layoutParams);
先说第一种情况,在setLayoutParams(layoutParams)方法中,调用了requestLayout()刷新重新布局,使新的LayoutParams生效。关于requestLayout()详见View的requestLayout()流程一文。
public void setLayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
if (params == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("Layout parameters cannot be null");
}
mLayoutParams = params;
resolveLayoutParams();
if (mParent instanceof ViewGroup) {
((ViewGroup) mParent).onSetLayoutParams(this, params);
}
requestLayout();
}为什么不调用setLayoutParams(layoutParams)方法,也能使修改后的LayoutParams生效?是因为LayoutParams是在布局阶段之前设置的,比如在onCreate()中进行操作,即便没有再次setLayoutParams(layoutParams),也会在后续的布局阶段生效。
相关资料:
reference/android/view/ViewGroup.LayoutParams
reference/android/view/ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams